
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone that plays a key role in regulating blood glucose levels, digestion, metabolism, and appetite. Here are some of the ways GLP-1 works:
Blood glucose: GLP-1 is an incretin hormone that helps control blood glucose levels by stimulating insulin secretion and inhibiting glucagon secretion.
Appetite: GLP-1 acts as a satiety factor that reduces food intake and curbs cravings.
GLP-1 is released in the gut after eating, and it also affects the hypothalamus, which is the part of the brain that controls feelings of fullness.
Other effects: GLP-1 also helps with digestion and gastric emptying.
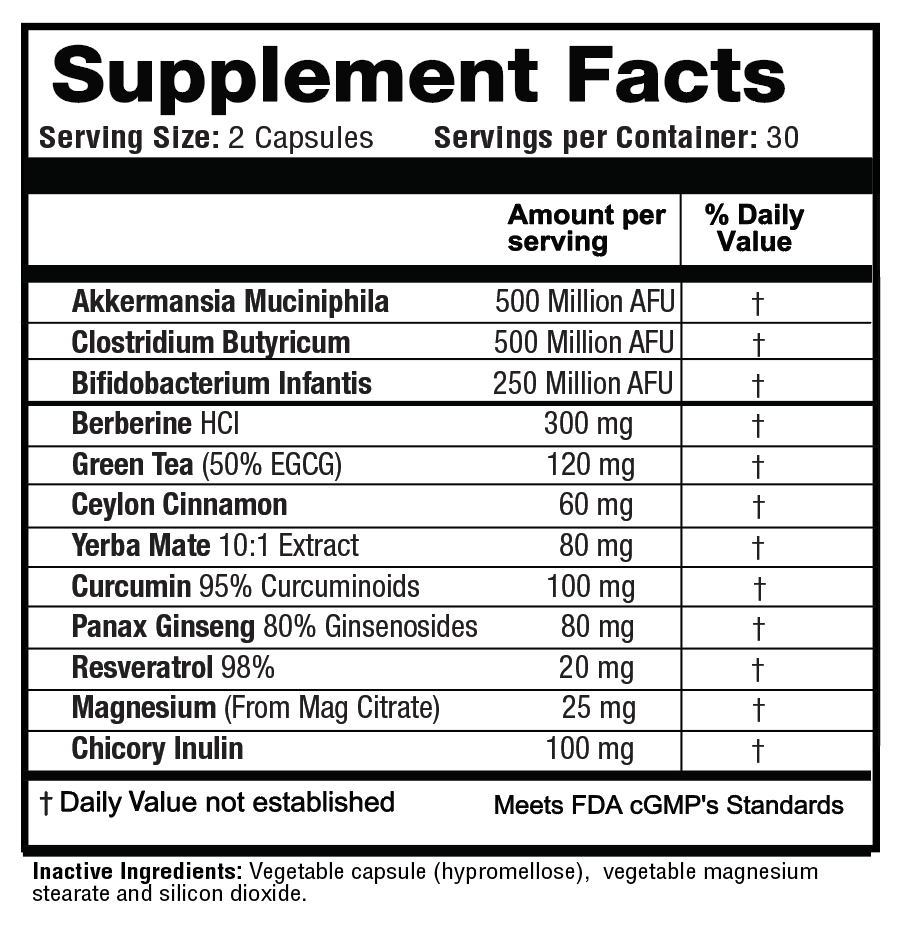
Probiotic Blend +
1.25 Billion AFU
GLP-1 is a naturally occurring hormone in the body that helps regulate appetite, food cravings, blood sugar, and digestion.
1LifeScience has formulated GLP-1 Pro to unlock the potential to boost GLP-1 production naturally within the body.*
Studies published in Journal Nature show the potential of probiotics including Akkermansia muciniphila to support GLP-1 levels. The GLP-1 Pro formula provides an unmatched, comprehensive blend of key probiotics, prebiotics, and herbs to support appetite control and curb food cravings.*
Taken with a sensible diet and light to moderate exercise, GLP-1 Pro can be an effective tool to support healthy weight management. *
Synthesis: GLP-1 is produced in the gut and brain from the proglucagon gene.
Duration: GLP-1's effects are short-lived, lasting only 1–2 minutes in the circulatory system.
Degradation: GLP-1 is broken down by dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4), which reduces its effectiveness.
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RA) can help with weight loss and may also promote bone formation.
What is the science behind GLP-1?
GLP-1 is released by the lining of the intestine in response to nutrient ingestion, particularly carbohydrates. It stimulates insulin secretion and, together with gastric inhibitory peptide, is one of the incretin hormones. It also slows gastric emptying.